Electric Field Lines and Equipotential Surfaces
Electric Field Lines and Equipotential Surfaces: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Electric Lines of Force, Properties of Electric Lines of Force, Equipotential Surfaces, Electric Field Lines due to a Positive Point Charge, Electric Field Lines due to a Negative Point Charge, etc.
Important Questions on Electric Field Lines and Equipotential Surfaces
Assertion: Two equipotential surfaces cannot cut each other.
Reason: Two equipotential surfaces are parallel to each other.
Assertion(A): Electric field is always normal to equipotential surfaces and along the direction of decreasing order of potential.
Reason (R): Negative gradient of electric potential is electric field.
Nature of equipotential surface for a point charge is
The instantaneous values of current and voltage in an circuit are given by . Then
In an ac circuit the current and the A.C. potential is Volt. Then the power consumed is.
The equipotential surface of an electric dipole is
What is the angle between the electric field and the plane of an equipotential surface?
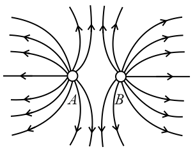
How the electric field lines due to two identical positive charges are different from the field lines due to two identical negative charges?
Which one of the following statements is not true for electric field lines due to two positive charges situated at a distance in space?
The electric field lines are drawn for two charges and situated at a distance in space, as shown below. Which one of the following statements is true for the charges and ?
Some equipotential surfaces, which are normal to - plane are shown in the adjoining figure the direction of the electric field is:
(A) 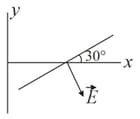
(B) 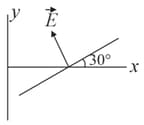
(C) 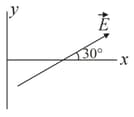
(D) 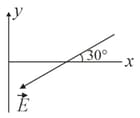
Draw the electric field lines in space due to a single negative charge.
Field lines due to a negative charge are
The statement "Electric field lines start from positive charge and end at negative charge" is
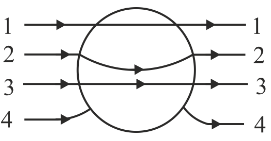
A solid metallic sphere is placed in a uniform electric field. The lines of force follow the path(s) (shown in figure) :-
What will be the work done in moving a charge from one point to another point at a distance of on an equipotential surface?
What is the shape of equipotential surface for the following: A uniform electric field
Write two properties of equipotential surface.
Show that no work is done in moving a test charge from one point to other on an equipotential surface
What is meant by equipotential surface. Draw equipotential surfaces for a point charge
